
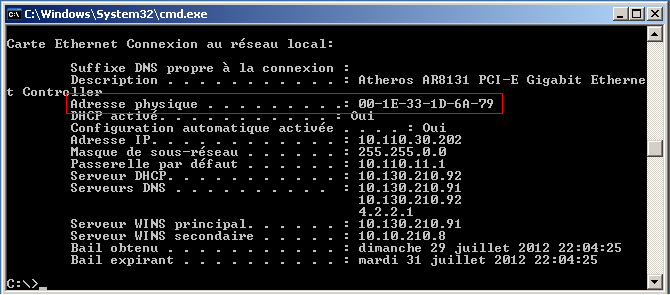
You should see a listing of information about all of your network cards.Type “ipconfig /all” at the command line and then hit enter.Press Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.Type “cmd” in the Run command window in the box labeled “Open:” This will open the Command Prompt.Press the Windows key + “R” to open the run command.Applicable cases may be to troubleshoot a specific device's connection or to add a device to an allow list of block list.īelow are the processes used to locate the MAC address of a Windows or Mac computer: Many times it is helpful to obtain the MAC address (Physical Address) of a client computer. For your IP address, from the tabs on the top, select “TCP/IP”.Finding the MAC Address of Windows or Mac Computer.For your MAC address, from the tabs on the top, select “Hardware”.From the options to the right, click the “Advanced” button.From the list on the left, highlight the option desired, e.g., “Wi-Fi” or “Ethernet”.From the Apple menu, select “System Preferences”.Your MAC address is the Physical Address listed, and your IP address is the IP address listed.The command will return information that looks like the following:ĭescription.
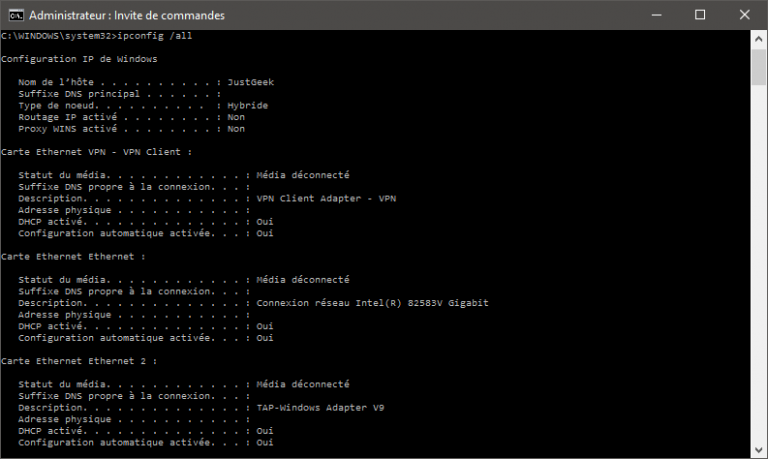
Within the command prompt, type “ipconfig/all”.Type “cmd” into the dialog box that appears, and click “Okay”.Select “Run” if available, or click into the search box on the start menu itself.The UW’s Network Portal displays basic information about your network connection, and should contain your MAC and IP addresses. The following methods will help you manually determine what your MAC and IP addresses are depending on the operating system you are running. On a computer network, a media access control (MAC) address is your computer’s unique identification number used by the network to identify your device, and your IP address is the online network address for your computer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
